
Domain: shared access to persistent representations.Application: shared processing of transient representations.Presentation: non shared processing of I/O.Of these, the domain layer seems to be the only one unambiguously set apart, definitions of the others leaving room for overlaps but potential qualms can be easily remedied by introducing formal criteria:
#Bounded context example software
With regard to software (as opposed to enterprise) architecture, DDD identifies four layers: users interfaces (or presentation), applications, domains (or models), and infrastructures. Setting DDD layers with regard to enterprise architecture could help to clarify the point. On that regard Domain Driven Design seems inconclusive: on one hand it insists upon the tie between concepts and implementations, on the other hand it makes a clear distinction between concepts (roots and aggregates), and their use (contexts). Feeding development processes is not the only purpose of descriptive models. But what may once have been a safe assumption is now a very hazardous one considering that today’s IT systems must be weaved with enterprise environment and accommodate continuously to its changes. Unfortunately, this seemingly benign neglect seems to imply that descriptive models have no other purpose than supporting the development of systems, which can subsequently stand on their own. Architecture LayersĪll too often, modelers overlook the difference between descriptive and prescriptive models, the former depicting business environments and objectives, the latter their symbolic representations in systems.

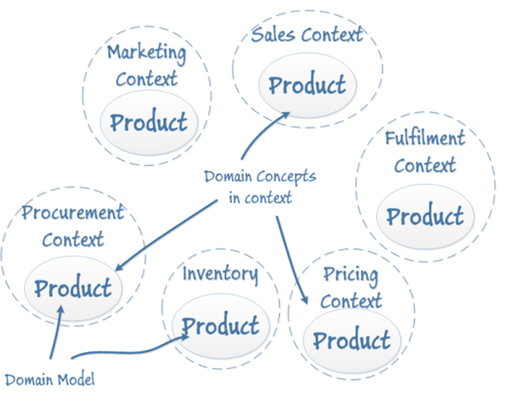
If the meaning and benefits of layers and aggregates are widely understood, there is less of a consensus about practical implementation of bounded contexts and ubiquitous languages.
#Bounded context example how to
How to conciliate bounded contexts and open minds (Balazs Szabo)įour basic tenets are often put ahead to characterize DDD: Domain Driven Design (DDD), the brainchild of Eric Evans, aims to map out system representations of business entities directly from business concepts and semantics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
